


Next: Hydrogenated amorphous carbon
Up: Examples of data contained
Previous: Amorphous magnesium silicate
Magnesium-aluminium spinel (MgAl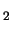 O
O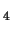 ) has been considered
as a primary condensate in the outflows of oxygen-rich AGB stars
and as a potential carrier of the 13
) has been considered
as a primary condensate in the outflows of oxygen-rich AGB stars
and as a potential carrier of the 13 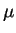 m emission band observed
in the spectra of these stars [11]. Therefore, in the
Jena laboratory, a systematic study of the infrared properties
of Mg-Al oxides of both synthetic and natural origin was performed
in order to derive the optical constants of these materials.
This led to the discovery of two accompanying features in the
astronomical spectra at larger wavelengths, thereby
strongly supporting the idea of spinel condensates in AGB star
outflows (see Fig.
m emission band observed
in the spectra of these stars [11]. Therefore, in the
Jena laboratory, a systematic study of the infrared properties
of Mg-Al oxides of both synthetic and natural origin was performed
in order to derive the optical constants of these materials.
This led to the discovery of two accompanying features in the
astronomical spectra at larger wavelengths, thereby
strongly supporting the idea of spinel condensates in AGB star
outflows (see Fig. ![[*]](file:/usr/local/lib/latex2html/icons/crossref.gif) , [12]).
Recently, the experiments have been extended in the direction
of Ca-Al oxide minerals [13] and condensation
studies of oxide grains in low-presure oxygen-rich atmospheres.
, [12]).
Recently, the experiments have been extended in the direction
of Ca-Al oxide minerals [13] and condensation
studies of oxide grains in low-presure oxygen-rich atmospheres.
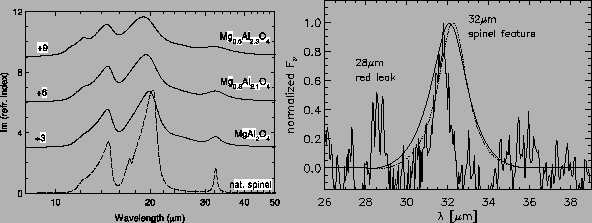
Figure:
Left panel: Imaginary part of the refractive index for synthetic
and natural magnesium-aluminium spinels. Right panel: Calculated normalized
absorption spectra for small particles composed of natural spinel
(smooth solid line) and synthetic MgAl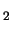 O
O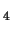 (dotted line)
in comparison to the band profile of the
newly discovered 32
(dotted line)
in comparison to the band profile of the
newly discovered 32 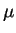 m feature [12]
m feature [12]
 |



Next: Hydrogenated amorphous carbon
Up: Examples of data contained
Previous: Amorphous magnesium silicate
root
2003-03-06

