


Next: Magnesium-aluminium oxide (spinel)
Up: Examples of data contained
Previous: Silicate minerals
About 85-90 % of the dust condensing in the envelopes
of oxygen-rich evolved stars consist of amorphous magnesium or
magnesium-iron silicates [6].
Optical constants (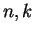 ) of stoichiometric and nonstoichimetric
magnesium silicates with Mg/Si ratios from 0.7 to 2.4 produced by
the sol-gel method have been derived from reflection measurements
by a combination of Kramers-Kronig analysis (KKR) and
Lorentz-oscillator fit method (see Fig.
) of stoichiometric and nonstoichimetric
magnesium silicates with Mg/Si ratios from 0.7 to 2.4 produced by
the sol-gel method have been derived from reflection measurements
by a combination of Kramers-Kronig analysis (KKR) and
Lorentz-oscillator fit method (see Fig. ![[*]](file:/usr/local/lib/latex2html/icons/crossref.gif) ). The
calculated absorption coefficients show that MgO influences
the position of the 10 and 20
). The
calculated absorption coefficients show that MgO influences
the position of the 10 and 20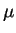 m band. With increasing MgO
content the 10
m band. With increasing MgO
content the 10 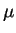 m band is shifted to longer wavelengths
whereas the 20
m band is shifted to longer wavelengths
whereas the 20 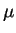 m band is shifted in the opposite direction.
m band is shifted in the opposite direction.
Figure:
Left panel: Imaginary part of the refractive index for
amorphous Mg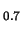 SiO
SiO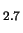 (dotted line) and Mg
(dotted line) and Mg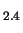 SiO
SiO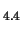 (solid line). Right panel: Absorption efficiency normalized by
particle radius calculated for a continuous distribution of
ellipsoidal grain shapes (CDE) composed of the same materials.
(solid line). Right panel: Absorption efficiency normalized by
particle radius calculated for a continuous distribution of
ellipsoidal grain shapes (CDE) composed of the same materials.
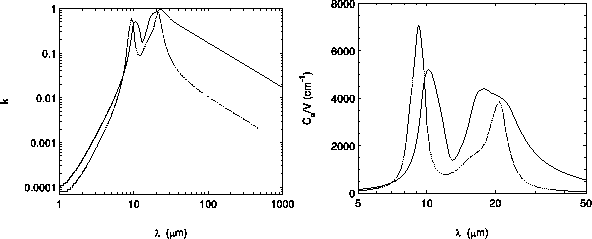 |
The comparison between differently produced magnesium silicates
demonstrates the existence of varying amorphous magnesium
silicates material with differences in the internal structures.
Based upon these results one has to conclude that the amorphous
state of any magnesium silicate is not unique but there exist
different possibilities for structural arrangements of subunits in
the amorphous silicate structure, similar to the varying
structures of amorphous carbon [10].
The astrophysical usefulness of these sol-gel silicates was tested
by comparison of optically thin model spectra based on the new
optical data with the dust emissivity derived from ISO-SWS spectra
of AGB stars in the range between 8-30  m. The dust
emissivity derived from TY Dra, an evolved dust forming star, can
excellently be reproduced by the models, sugessting that the dust
grains consist indeed of pure amorphous Mg silicate.
m. The dust
emissivity derived from TY Dra, an evolved dust forming star, can
excellently be reproduced by the models, sugessting that the dust
grains consist indeed of pure amorphous Mg silicate.



Next: Magnesium-aluminium oxide (spinel)
Up: Examples of data contained
Previous: Silicate minerals
root
2003-03-06

