- ...
medium1
- Crystalline graphite has a strong resonant feature
near
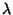 11.52
11.52 (Draine, [1984]) which is
not observed.
(Draine, [1984]) which is
not observed.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... width2
- Note that the observed weakness
of the bump strength in dense clouds can be attributed to the
hydrogenation of carbon (Sorrell, [1990]).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
Gold-type3
- Its idea was first suggested by
Gold ([1952]).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...fpell)4
- A similar
conclusion follows from calculations made by Matsumura and Seki ([1996]).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... ``correct''5
- ``Correctness''
is contained in the use of the measured optical constants for which
real and imaginary parts are already connected by Kramers-Kronig relations
but not a wavelength-independent refractive index.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.